It sounds too good to be true - not to mention the fact that it violates almost every known law of physics.
But British scientists claim they have invented a revolutionary device that seems to 'create' energy from virtually nothing.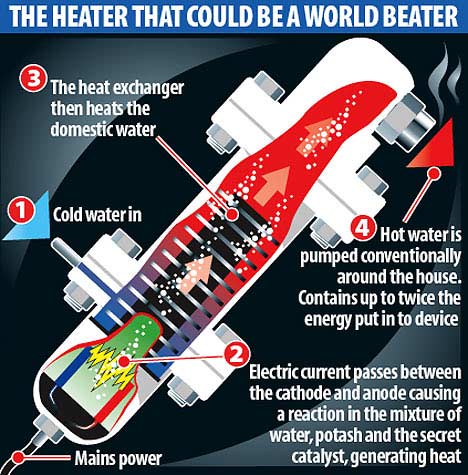
Their so-called thermal energy cell could soon be fitted into ordinary homes, halving domestic heating bills and making a major contribution towards cutting carbon emissions.
Even the makers of the device are at a loss to explain exactly how it works - but sceptical independent scientists carried out their own tests and discovered that the 12in x 2in tube really does produce far more heat energy than the electrical energy put in.
The device seems to break the fundamental physical law that energy cannot be created from nothing - but researchers believe it taps into a previously unrecognised source of energy, stored at a sub-atomic level within the hydrogen atoms in water.
The system - developed by scientists at a firm called Ecowatts in a nondescript laboratory on an industrial estate at Lancing, West Sussex - involves passing an electrical current through a mixture of water, potassium carbonate (otherwise known as potash) and a secret liquid catalyst, based on chrome.
This creates a reaction that releases an incredible amount of energy compared to that put in. If the reaction takes place in a unit surrounded by water, the liquid heats up, which could form the basis for a household heating system.
If the technology can be developed on a domestic scale, it means consumers will need much less energy for heating and hot water - creating smaller bills and fewer greenhouse gases.
Jim Lyons, of the University of York, independently evaluated the system. He said: 'Let's be honest, people are generally pretty sceptical about this kind of thing. Our team was happy to take on the evaluation, even if to prove it didn't work.
'But this is a very efficient replacement for the traditional immersion heater. We have examined this interesting technology and when we got the rig operating, we were getting 150 to 200 per cent more energy out than we put in, without trying too hard. Read

